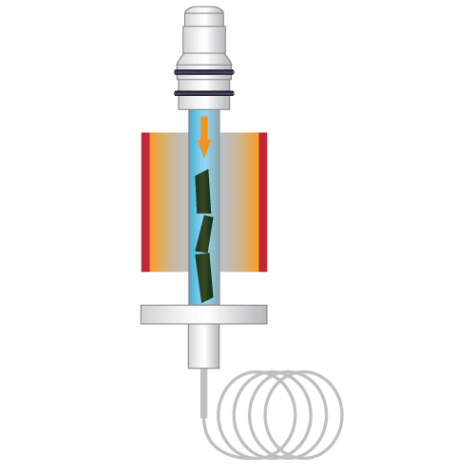
Flash-VASE™ provides for precise analysis of VOCs & SVOCs in matrices with low volatility.
Compare All Sorbent Pen Extraction Techniques For Complete Coverage of VOC to SVOC Analysis Of Virtually Any Matrix
Definitions:
Open System - Unretained compounds/gases allowed to pass through sorbent for removal by pump/vacuum.
Closed System - Completely isolated during extraction, so breakthrough of even the lightest compounds isn't possible. Allows recovery of wider boiling point compounds.
Flash-VASE. What Is It?
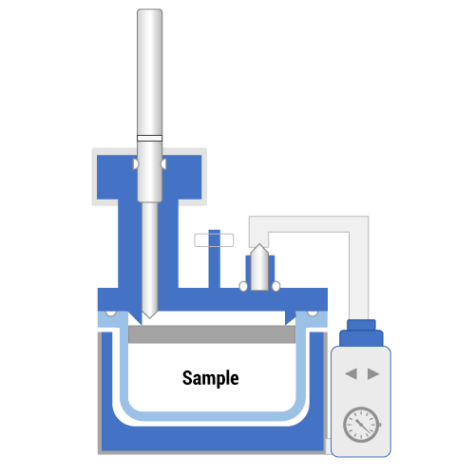
Flash-VASE is a next generation Thermal Extraction technique that places the sample in very close proximity to the collection sorbent, and uses static extraction under vacuum to more efficiently and completely recover volatile through semi-volatile compounds. Flash-VASE places the sample within a few centimeters of the collection sorbent, with no flowing gases to heat up the sorbent during the extraction which is a known problem with dynamic headspace techniques, so the collected compounds stay optimally close to the front of the sorbent bed for fast and complete release to the GC. Extraction under a vacuum allows recovery of chemicals at a lower temperature, reducing or avoiding breakdown of the matrix itself. Flash-VASE has a tremendous number of advantages over other thermal extraction techniques, allowing Chemists to truly “See What’s Really There™”, in a way that keeps the analytical system clean and free from carryover.
Flash-VASE is intended for samples containing relatively low moisture and solvent levels, as the sample is heated anywhere from 30 °C to 330 °C while in a closed system, so the potential for generating a substantial amount of vapor during Thermal Extractions should be considered. However, small amounts of water can be Flashed onto the Sorbent Pen with removal afterwards either by cooling the vial on a cold tray to pull water back down out of the Pens, or by placing a vacuum on the Pens to pull the water off prior to thermal desorption into a GCM

Extreme Precision, By Design
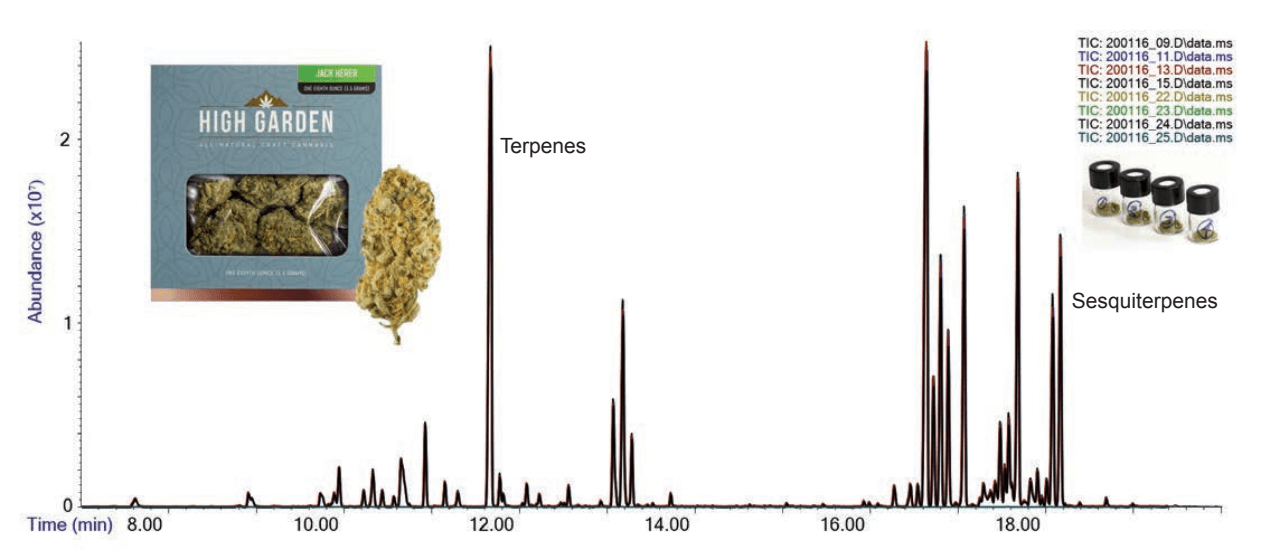
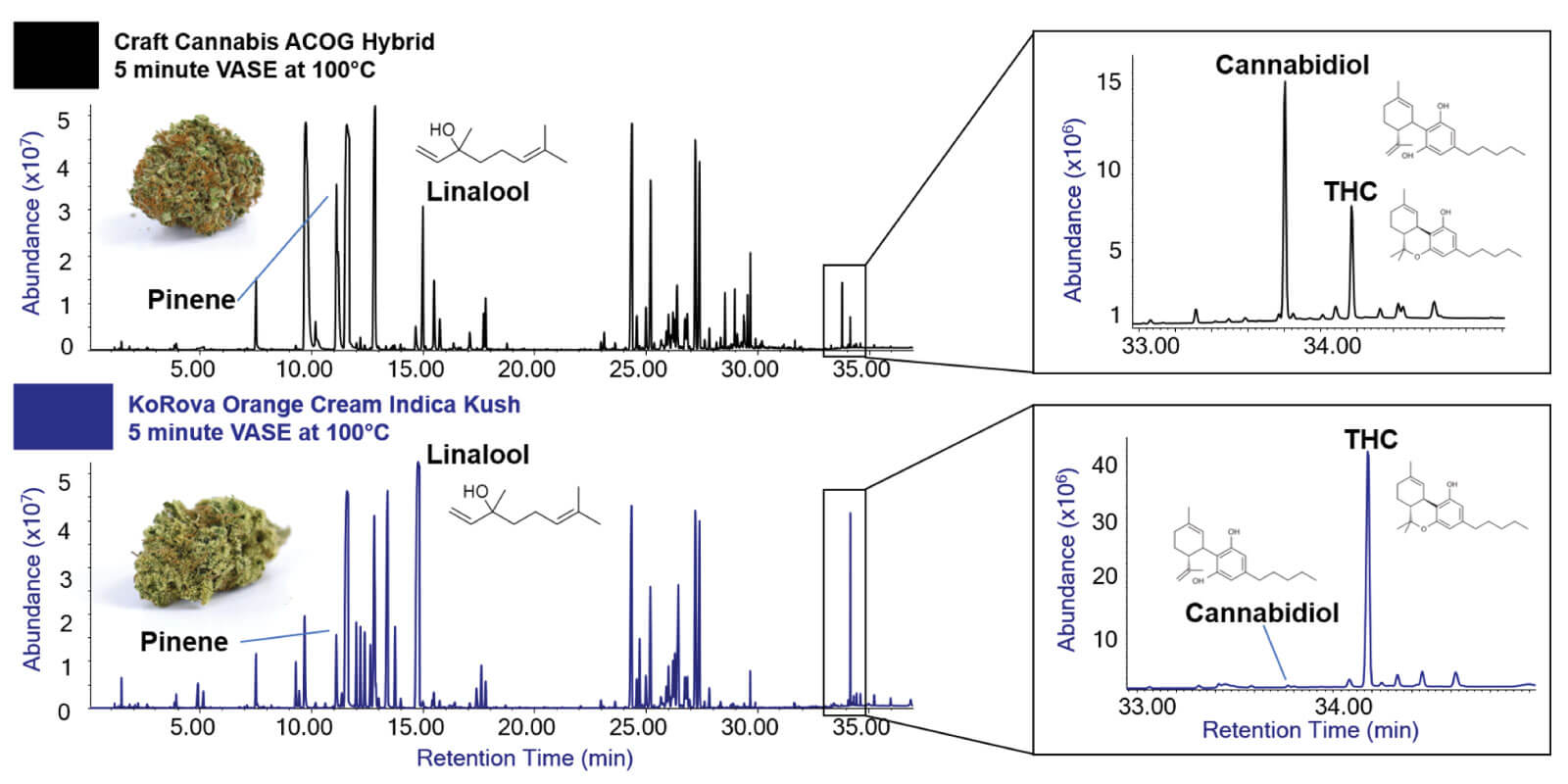
Flash-VASE provides incredibly reproducible results, by eliminating the inconsistencies inherent in dynamically purged Thermal Extractions. Below is an example of 8 replicate Cannabis analyses for Monoterpene and Sesquiterpene profiling, and these 8 runs almost perfectly overlap. The Flash-VASE extraction times in these examples was just 5 minutes, at 100 °C. Higher temperatures will yield reproducible recovery of the Cannabinoids present in Cannabis.
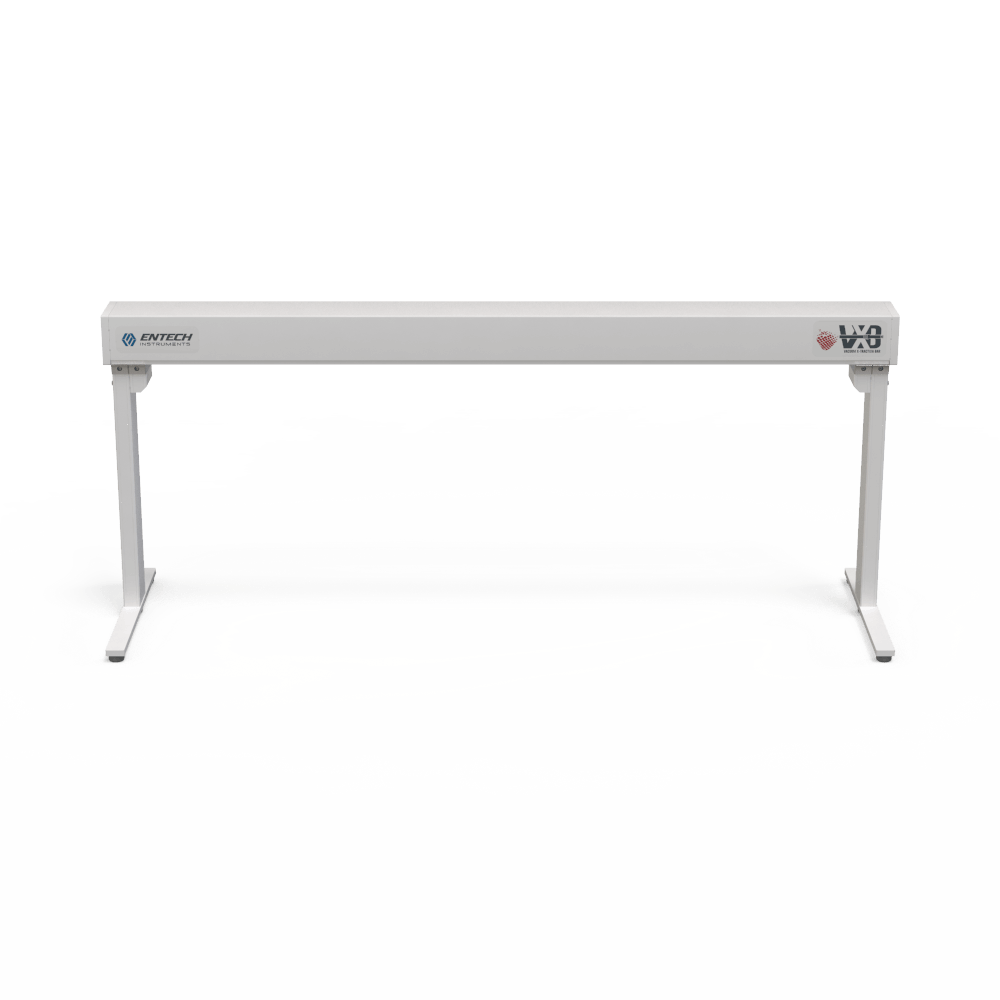
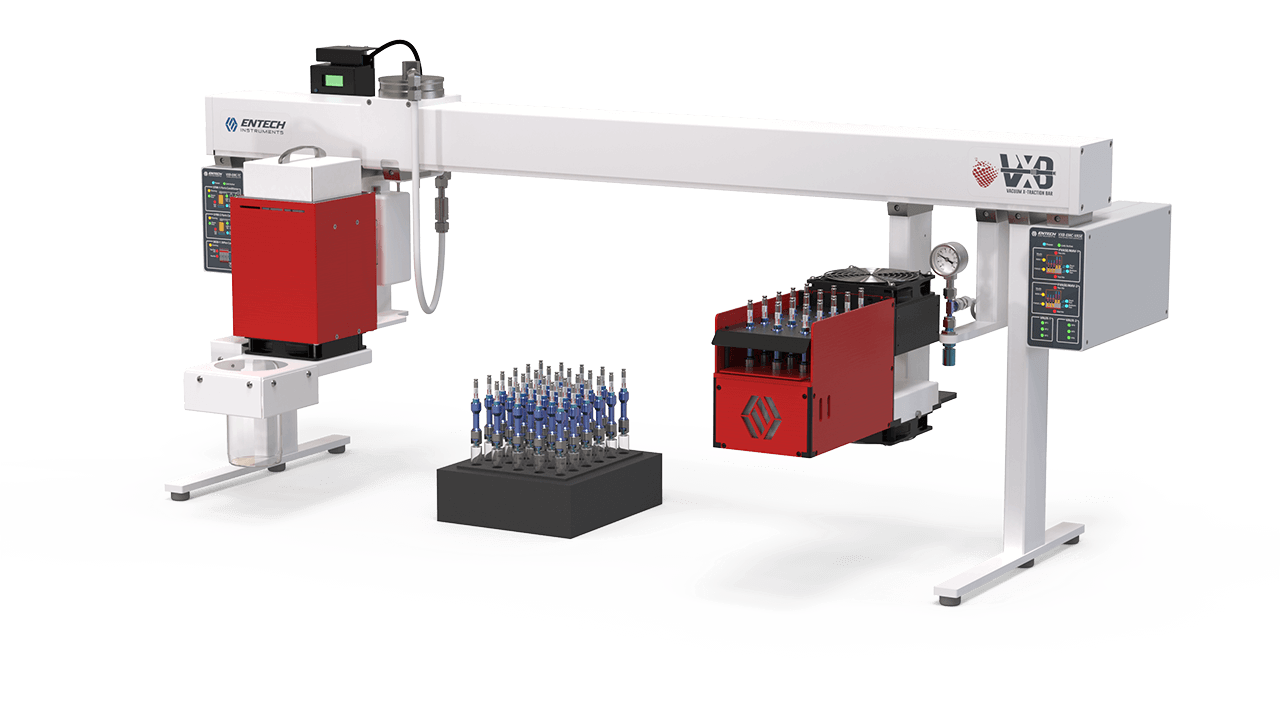
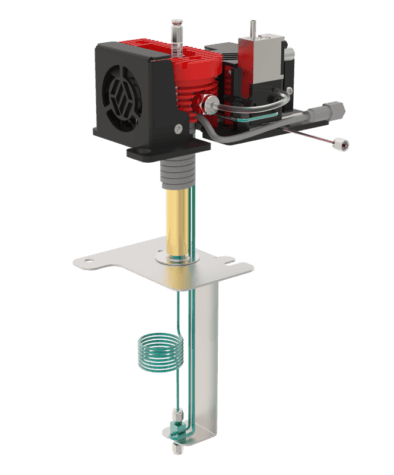
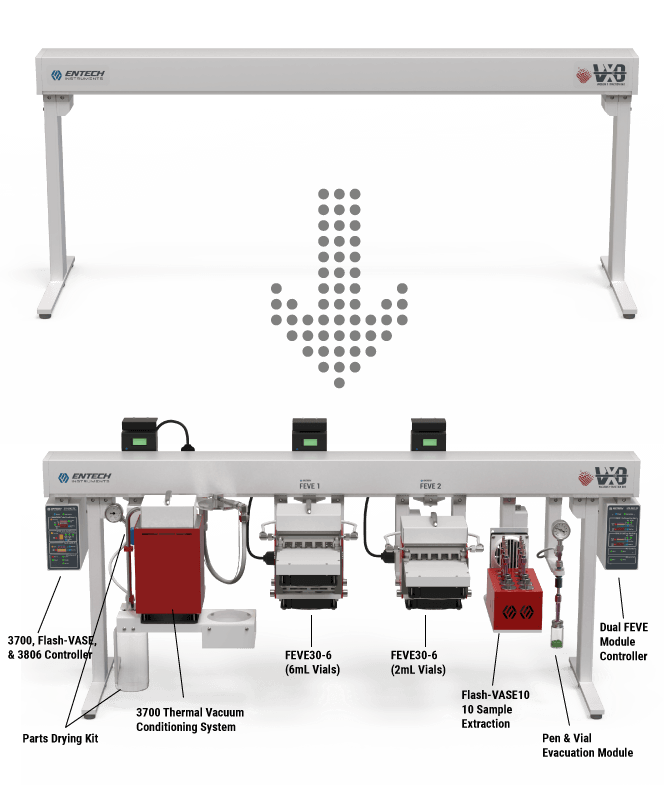
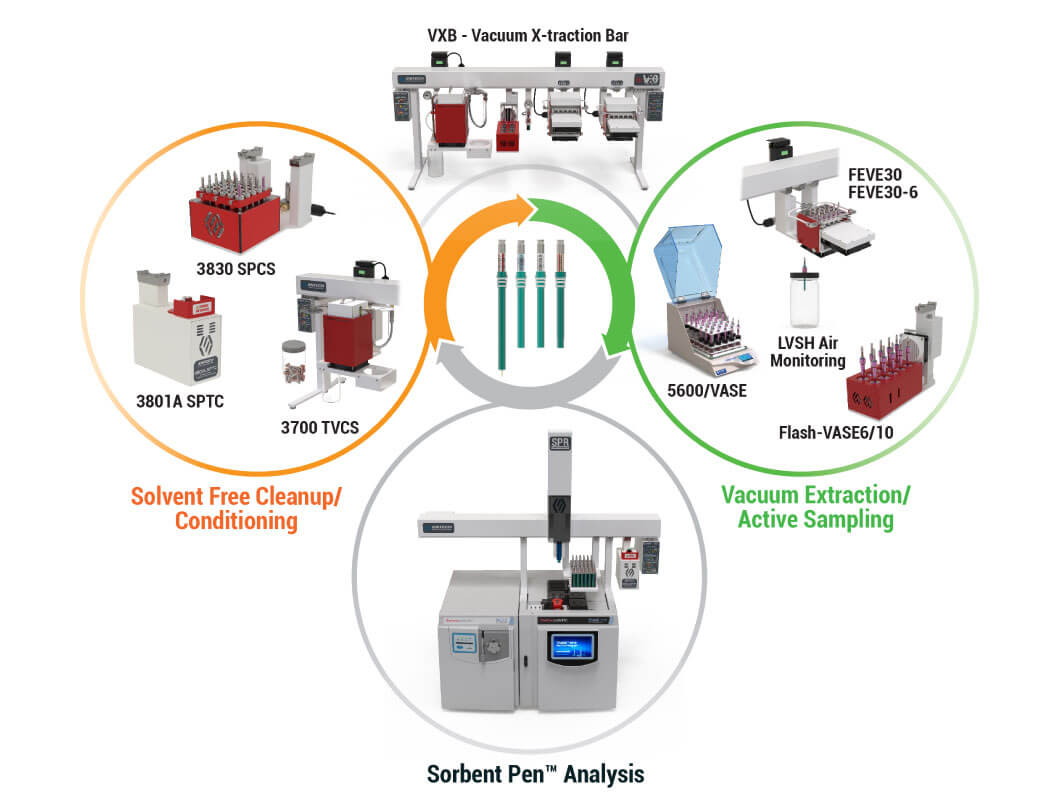
Flash-VASE utilizing the Vacuum X-traction Bar (VXB)
The Vacuum X-traction Bar (VXB) supports sample extraction onto Sorbent Pens and the cleanup of associated extraction hardware (sleeves, O-rings, etc). The VXB allows extractions to be performed in the sample preparation area, with only the extracts on Sorbent Pens brought into the GCMS laboratory. This is similar to how sample preparation techniques are currently performed, except the Entech vacuum extraction methods are easier, cleaner, and more sensitive, all without the use of hazardous solvents. The VXB comes in 30” and 50” sizes, allowing for convenient above the bench management of the Flash-VASE Modules. Other modules may also be connected, such as the 3700 Thermal Vacuum Cleaning System, which is utilized to restore background-free extraction hardware before performing the next set of extractions.
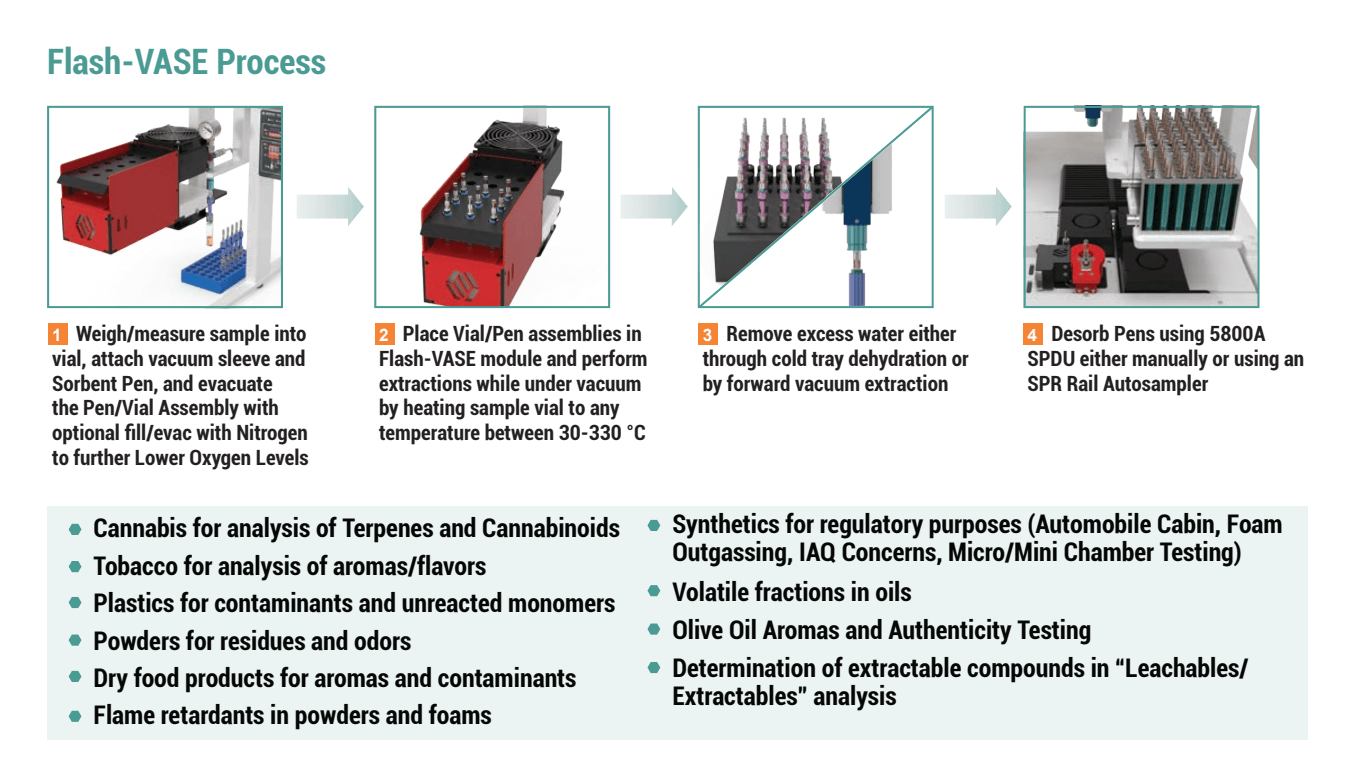
The list of applications is quite extensive, and Flash-VASE can be scaled up to look at outgassing from larger samples as needed, such as in forensic investigations of accelerants in fire debris. Just as in VASE, the presence of a vacuum increases the rate of evolution of volatiles out of materials at lower temperatures, and depending on the matrix or sample surface area, the extraction times can be as short as 5-15 minutes (Cannabis) by heating the sample to 100 – 200 °C under vacuum. This provides a whole new opportunity for high speed sample throughput for Flash-VASE compatible applications.
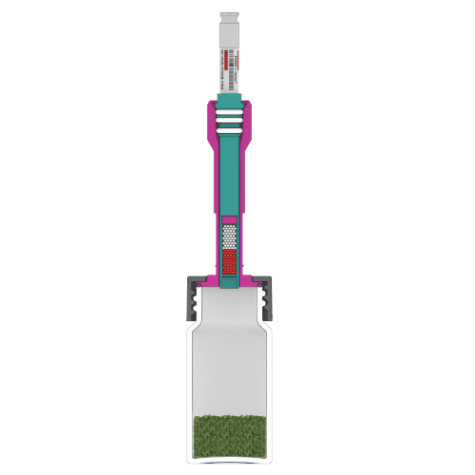
Sorbent Pen Options
Sorbent Pen Desorption and Analysis Solutions.
Flash-VASE Modules & Pumps
| Image (click to enlarge) | Part # | Description | Unit | link to product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VRES | Vial Heater Module, VASE Rail Extraction System, 120VAC/60Hz | EA | ||
| VRES-HV | Vial Heater Module, VASE Rail Extraction System, 240VAC/50Hz | EA | ||
| VRES-FVVM-2ML | 2mL vial Flash-VASE Vial Module | EA | ||
| VRES-FVVM-6ML | 6mL vial Flash-VASE Vial Module | EA | ||
| VRES-FVVM-20ML | 20mL vial Flash-VASE Vial Module | EA | ||
 |
10-20100 | 2-Stage Oilless Diaphragm Pump, Dual Voltage 120/240VAC, 50-60Hz | EA | Product Page |
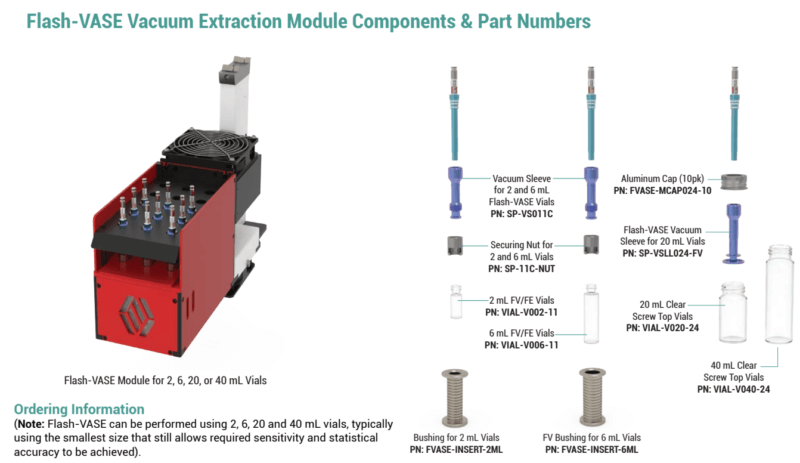
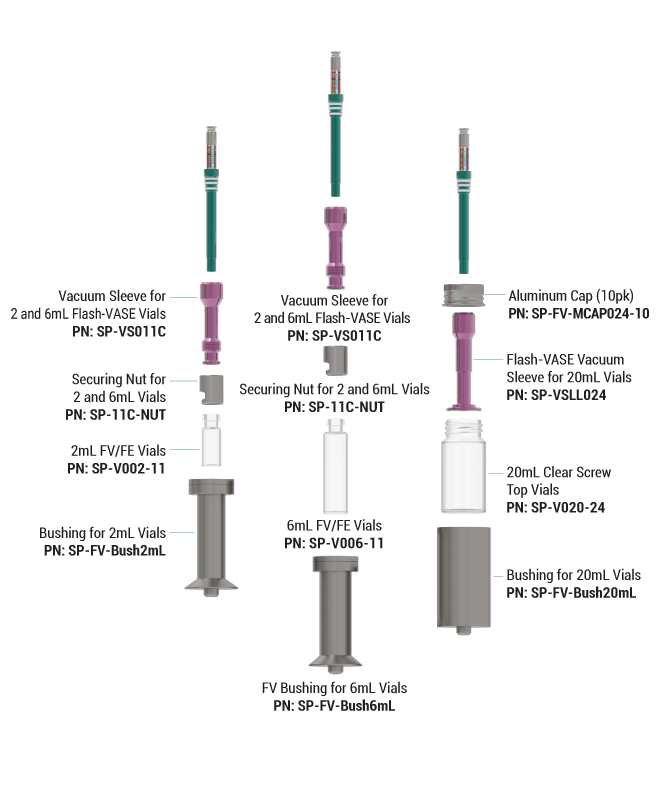
Flash-VASE Extraction Vials, Sleeves, Components, and Accessories
| Image (click to enlarge) | Part # | Description | Unit | link to product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2mL Flash-VASE Components | ||||
| VIAL-V002-11 | 2mL Clear Vials, wide mouth 11mm Crimp Top | 100pk | ||
| SP-VS011C | Vacuum Sleeve for 2 / 6mL Flash-VASE, EEU Module | 10pk | ||
| SP-11C-NUT | Securing Nut for 11mm Crimp Top Vial (2mL and 6mL) | 10pk | ||
| OR-L011S-30 | 2mL Vial Vacuum Sleeve Silicone O-rings | 30PK | ||
| 6mL Flash-VASE Components | ||||
| VIAL-V006-11 | 6mL Clear Flash-VASE Vials | 100pk | ||
| SP-VS011C-10 | Vacuum Sleeve for 2 and 6mL Flash-VASE Vials | 1 | ||
| SP-11C-NUT | Securing Nut for 11mm Crimp Top Vial (2mL and 6mL) | 1 | ||
| OR-L011S-30 | 6mL Vial Vacuum Sleeve Silicone O-rings | 30pk | ||
| 20mL Flash-VASE Components | ||||
| VIAL-V020-24 | 20mL x 24-400 Clear Screw Top Vial | 144pk | ||
| VIAL-V020-24-A | 20mL x 24-400 Amber Screw Top Vials | 144pk | ||
| SP-VSLL024-FV-10 | Flash-VASE Vacuum Sleeve for 20mL Vials | 10pk | ||
| FVASE-MCAP024-10 | Aluminum Caps for 20mL Vials | 10pk | ||
| OR-L024S-3 | Clean High Temp Silicone O-rings for 20mL vial Vac Sleeves | 30pk |
VXB - Vacuum X-traction Bars
| Image (click to enlarge) | Part # | Description | Unit | link to product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
 |
SP-VXB-50 | Vacuum X-traction Bar (50” VXB), allows 3-4 modules to be attached simultaneously | EA | Product Page |
 |
SP-VXB-30 | Vacuum X-traction Bar (30” VXB), allows 1-2 modules to be attached simultaneously | EA | Product Page |
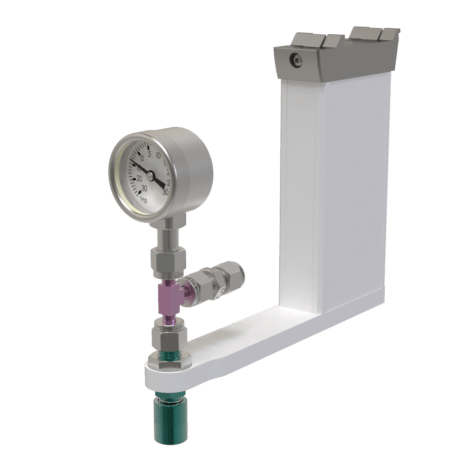 |
SP-VXB-PV-EVAC | Pen/Vial VXB Evacuation Module | EA | Product Page |
Cold Dehydration Tray and Accessories
| Image (click to enlarge) | Part # | Description | Unit | link to product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water Management | ||||
| SP-HSCOLDTRAY45-FV | Flash-VASE Cold Tray for Dehydration of 15 each of 2, 6, 20mL Vial | EA | ||
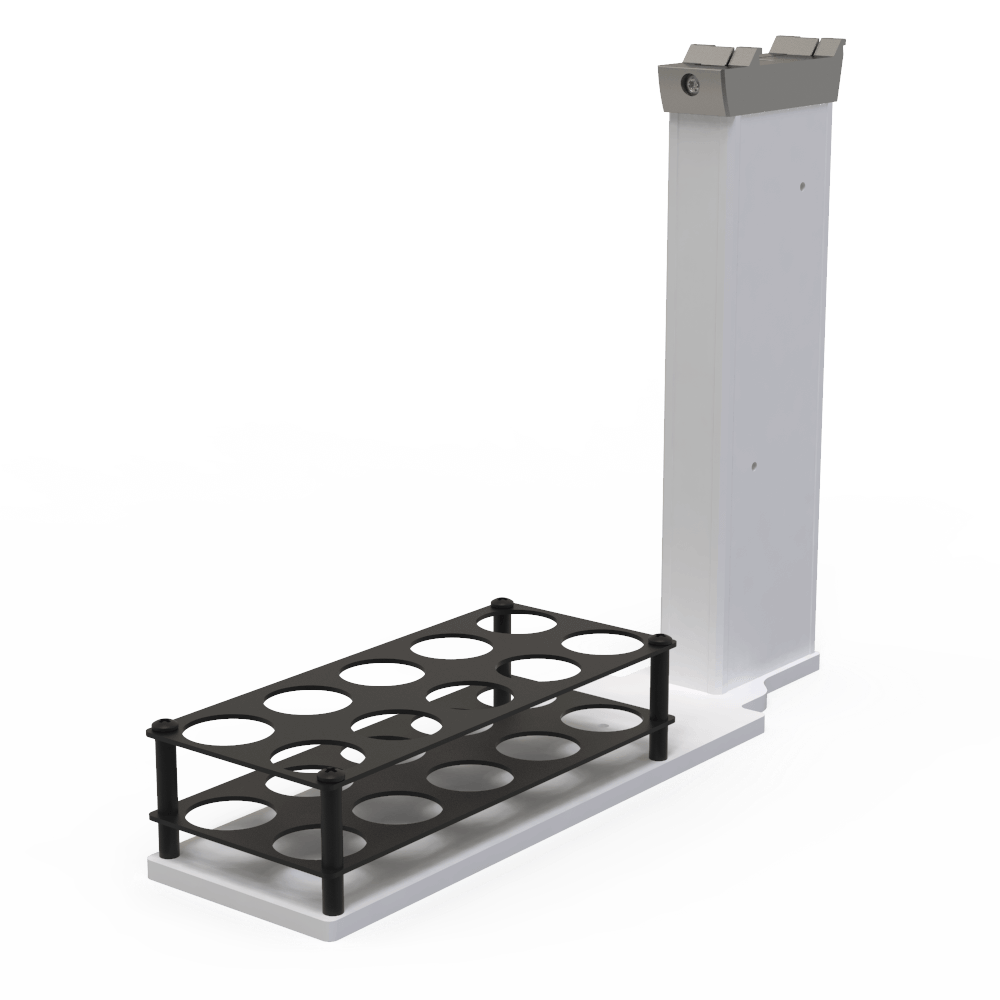
Vial Platforms and Trays
| Image (click to enlarge) | Part # | Description | Unit | link to product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
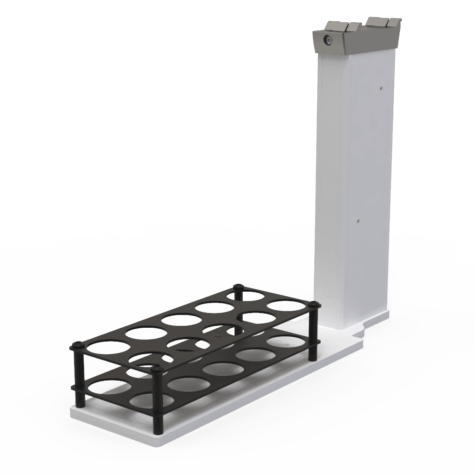 |
SP-PF-TRAY10-20M | 10-Position Platform/Tray for VXB/SPR40, 20/40mL Vials | EA | Product Page |
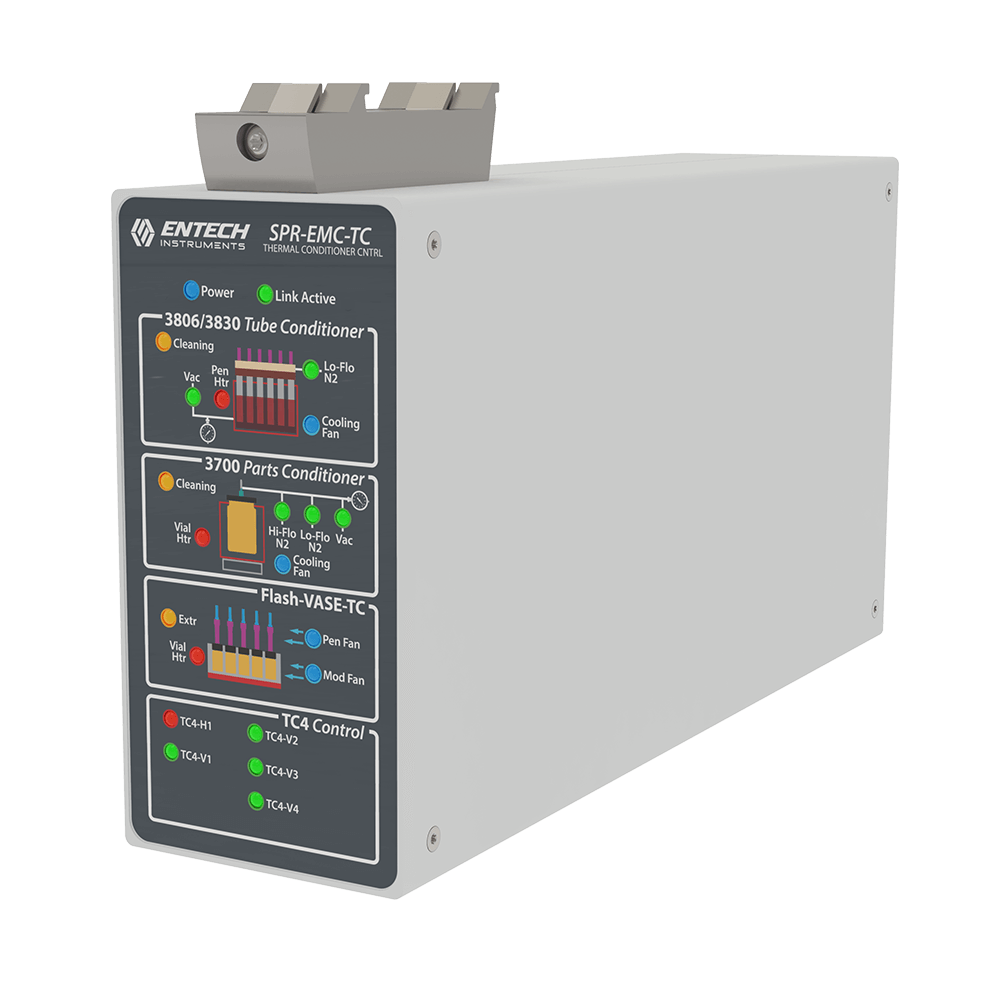
Flash-VASE Controllers
| Image (click to enlarge) | Part # | Description | Unit | link to product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Supports Flash-VASE, 3700, & 3830 | ||||
| VXB-EMC-VASE-12 | VXB Mounted Dual Controller for Flash-VASE 1/2 with SPRINT Interface, 120VAC/60Hz | EA | ||
| VXB-EMC-VASE-12-H | VXB Mounted Dual Controller for Flash-VASE 1/2 with SPRINT Interface, 240VAC/50Hz | EA | ||
| VXB-EMC-VASE-34 | VXB Mounted Dual Controller for Flash-VASE 3/4 with SPRINT Interface, 120VAC/60Hz | EA | ||
| VXB-EMC-VASE-34-HV | VXB Mounted Dual Controller for Flash-VASE 3/4 with SPRINT Interface, 240VAC/50H | EA |
Replacement O-rings
| Image (click to enlarge) | Part # | Description | Unit | link to product |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High-Temp O-rings (>180° C) | ||||
| SP-OR-1565S-30 | 2/6mL Vial Vacuum Sleeve Silicone O-rings | 30pk | Product Page | |
| SP-OR-L024S-30 | 20/40mL Vial Vacuum Sleeve Silicone O-rings | 30pk | Product Page | |
| Low Bleed O-rings (<180° C) | ||||
| SP-OR-1565F-30 | 2/6mL Vial Vacuum Sleeve FKM O-rings | 30pk | Product Page | |
| SP-OR60-L024-30 | 20/40mL Vial Vacuum Sleeve FKM O-rings | 30pk | Product Page |


Flash-VASE: A Safer and Better Way to do Thermal Extraction
Many systems attempt to perform thermal extraction by placing a sample into a tube and then directly thermally desorbing it into a GC. However, there are several draw-backs associated with this approach:
 Samples may not transfer quickly from the sample to a GC column since chemicals of interest will not release very fast from many matrices, causing poor peak shape unless a secondary trapping or focusing system is used
Samples may not transfer quickly from the sample to a GC column since chemicals of interest will not release very fast from many matrices, causing poor peak shape unless a secondary trapping or focusing system is used- Therefore, direct desorption methods often have to heat samples hotter to reduce band broadening, but higher temperatures will increase thermal degradation of the target compounds and the matrix
- Liberated compounds must remain in contact with the matrix longer during a pre-heating step, rather than allowing their removal once they become mobile
- Chemicals must diffuse out of the matrix at positive GC carrier gas pressures which slows down outgassing rates relative to a vacuum thermal extraction approach
 Samples with a high volatiles content can backflash into the GC carrier gas delivery lines, permanently contaminating the lines until the entire injection system is removed and solvent rinsed.
Samples with a high volatiles content can backflash into the GC carrier gas delivery lines, permanently contaminating the lines until the entire injection system is removed and solvent rinsed. Many matrices simply cannot be heated to GC injection temperatures, even momentarily, without changing them chemically, potentially creating artifact chemicals that were not in the original sample
Many matrices simply cannot be heated to GC injection temperatures, even momentarily, without changing them chemically, potentially creating artifact chemicals that were not in the original sample There is no water/moisture management opportunities when directly desorbing a sample into a GCMS
There is no water/moisture management opportunities when directly desorbing a sample into a GCMS Loading a sample into a 1/4” glass tube before direct desorption is more difficult than loading it into a vial, and some sample may drop into the desorber or injector, creating a background until removed
Loading a sample into a 1/4” glass tube before direct desorption is more difficult than loading it into a vial, and some sample may drop into the desorber or injector, creating a background until removed
Flash-VASE solves all of these problems by performing an offline vacuum thermal extraction, followed by a moisture removal step if necessary using either a cold plate or applied vacuum once the Pen is removed from the sample vial. This not only improves the performance of thermal extraction solutions, Flash-VASE may be the only way to perform thermal extraction on many thermally labile matrices.
Flash-VASE Improves Performance over Off-Line Dynamic Thermal Extraction
Other thermal extraction systems use small chambers or micro chambers which attempt to thermally extract samples by heating them, flowing a gas over them, and delivering the desorb gas through an outlet port/fitting and into a classical sorbent tube. There are numerous problems associated with this approach as well:
 The cell or chamber can become contaminated when exposed to higher concentration samples
The cell or chamber can become contaminated when exposed to higher concentration samples Difficulty in removing contamination in tubing/fittings between the chamber and the TD Tube
Difficulty in removing contamination in tubing/fittings between the chamber and the TD Tube Loss of high volatility compounds that breakthrough the sorbent in this “open” system
Loss of high volatility compounds that breakthrough the sorbent in this “open” system Loss of low volatility compounds that adsorb to surfaces prior to reaching the TD tube
Loss of low volatility compounds that adsorb to surfaces prior to reaching the TD tube Heating of the front of the sorbent bed can occur when trying to maintain a hot transfer system all the way to the collection sorbent. Hot gas introduced onto a sorbent will allow compounds to penetrate further into the sorbent, resulting in lower thermal desorption recoveries and greater potential for carryover
Heating of the front of the sorbent bed can occur when trying to maintain a hot transfer system all the way to the collection sorbent. Hot gas introduced onto a sorbent will allow compounds to penetrate further into the sorbent, resulting in lower thermal desorption recoveries and greater potential for carryover Channeling Effects are exhibited while flowing through a sorbent trap, causing reduced recovery, increased carryover, and increased thermal degradation by requiring higher desorption temperatures during analysis
Channeling Effects are exhibited while flowing through a sorbent trap, causing reduced recovery, increased carryover, and increased thermal degradation by requiring higher desorption temperatures during analysis
Flash-VASE eliminates these concerns as well. A glass vial is the entire “sample chamber”, which is used once and discarded, so no chance of carryover. There are no transfer lines and connective fittings in the flow path, as the opening of the Sorbent Pen is right at the top of the vial. There is no hot carrier gas to heat up the sorbent, so the penetration of compounds into the sorbent is far less, making their recovery during thermal desorption more complete and at lower desorption temperatures. The Flash-VASE closed system means that even very light compounds will be recovered, as long as they have more affinity for the sorbent in the Pen than they do for the heated sample matrix. Finally, the extraction occurs diffusively, eliminating channeling and all of the negative effects this has on recovery, carryover, and sampler lifetimes.
Compare All Sorbent Pen Extraction Techniques For Complete Coverage of VOC to SVOC Analysis Of Virtually Any Matrix